Troubleshooting
This guide helps you troubleshoot various situations you might encounter when working with Unleash feature flags, including flags not being returned, users not being exposed as expected, unexpected A/B test results, and CORS errors.
My feature flag is not returned or my users are not exposed
If a feature flag isn't being returned by the Frontend API or Edge, or if users are not being exposed to a flag you believe is enabled, consider the following. By default, these endpoints do not return feature flags that are not enabled to save bandwidth.
Initial checks
Verify feature configuration
- Ensure the feature flag has an activation strategy associated with it that will evaluate to
truefor your given context. - Confirm that the feature flag has been enabled in the specific environment your client application is using. (ref: enabling a feature flag)
SDK ready event (frontend clients)
- Ensure your application, especially frontend clients, waits for the SDK to emit the
readyevent before callingisEnabled('feature-flag')or attempting to get variant information. Calling these functions too early might mean the client hasn't yet received the latest flag configurations from the server.
Token configuration
Check token type
- To connect to the Frontend API or Edge, you must use a Front-end API token. Other token types will not work.
Check token access
- The token's access configuration is immutable after creation and defines which feature flags it can access. The format of the token indicates its scope:
- Access to all projects (current and future): Tokens starting with
*:(e.g.,*:production:xyz123etc...) provide access to flags in the specified environment across all projects. - Access to a discrete list of projects: Tokens starting with
[]:(e.g.,[]:production:xyz123etc...) grant access to a specific subset of projects in the given environment. You can see which projects a token has access to on the API Tokens page in the Unleash admin UI. - Single project access: Tokens starting with a project name (e.g.,
my_fullstack_app:production:xyz123etc...) are restricted to that project and environment.
- Access to all projects (current and future): Tokens starting with
Context and stickiness
Gradual rollout strategy and stickiness
- When using a gradual rollout strategy, pay close attention to the stickiness configuration.
- If the context provided by your SDK during flag evaluation does not include the field specified for stickiness (e.g.,
userId,sessionId, or a custom field), the gradual rollout strategy will evaluate tofalse. Consequently, the flag (or the "on" state for that user) will not be returned by the API.
Using the Unleash playground
- Feature activation strategies can be combined in complex ways. The Unleash Playground is an invaluable tool. You can use an access token along with various context values (input via the UI) to simulate how a flag will be resolved for different users and scenarios, helping you verify your configuration.
Alternative: Using variants for disabled/enabled states
If you need to know about a flag regardless of whether it's "on" or "off" for a user (e.g., for analytics or UI rendering logic), consider using variants:
-
First, enable the feature flag itself in the desired environment.
-
Next, configure strategy variants to represent "enabled" and "disabled" states. You can assign percentages to these variants (e.g., 50% "enabled", 50% "disabled").
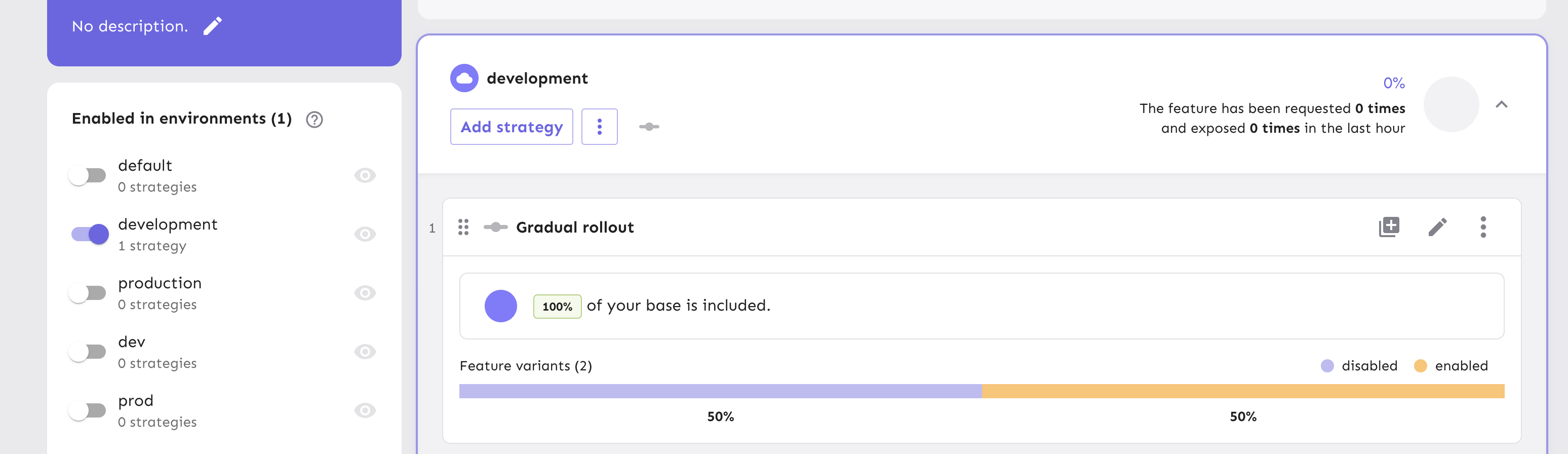 This flag itself is enabled in development and adds a 50%/50% split between disabled/enabled variants. This is essentially the same as a gradual rollout of 50% but using variants.
This flag itself is enabled in development and adds a 50%/50% split between disabled/enabled variants. This is essentially the same as a gradual rollout of 50% but using variants. -
Then, in your SDK, use the
getVariant()call (or equivalent) instead ofisEnabled(). -
This approach can also be combined with more complex constraint-based targeting.
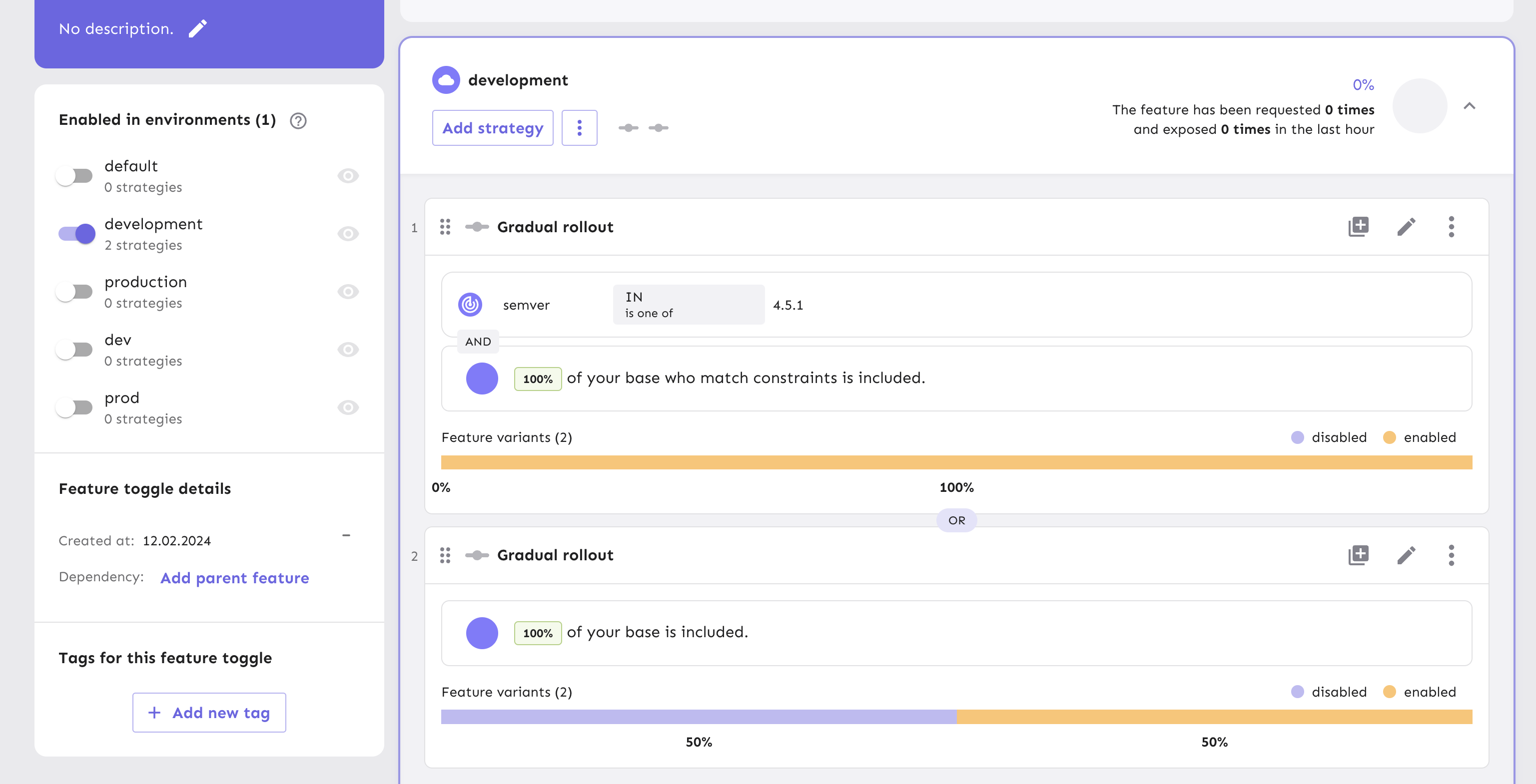 This flag returns an "enabled" variant for clients with a specific
This flag returns an "enabled" variant for clients with a specific semverand performs a percentage split for the remaining clients.
My A/B tests are producing unexpected results
If your A/B tests or experiments are producing unexpected results:
Prerequisite check
- First, ensure the feature flag is being returned correctly by following the guidance in the "My feature flag is not returned or my users are not exposed" section above.
Verify gradual rollout percentage
- Check the rollout percentage of your gradual rollout activation strategy. If you intend to include 100% of your user base in the A/B/n test, ensure the rollout percentage is set to 100%.
Check stickiness and context
- Revisit the stickiness configuration.
- If using default stickiness, confirm that either
userIdorsessionId(or both, depending on your setup) is consistently provided in the Unleash context from your application. - If the context provided during flag evaluation does not include the field used for stickiness, the gradual rollout strategy will evaluate to
false, and the user will not be part of the A/B test population for that flag.
- If using default stickiness, confirm that either
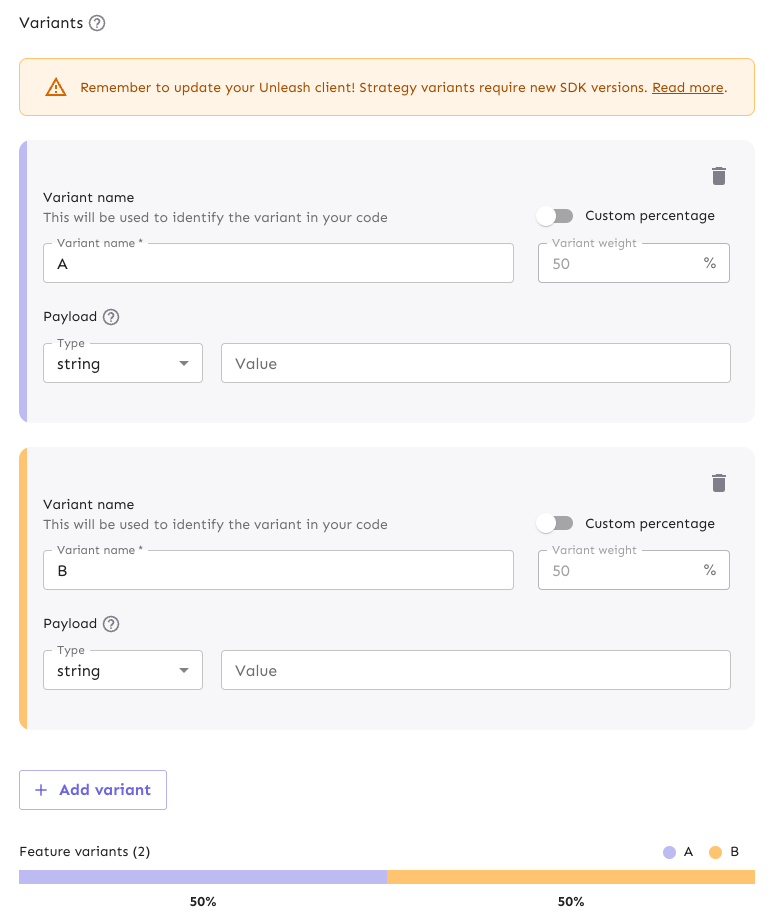
Ensure variants are correctly configured
-
Refer to the documentation on feature flag variants.
-
For a simple 50-50 A/B test, your variants should be configured accordingly (e.g., two variants, "A" and "B", with appropriate weighting or rollout distribution if not handled by a parent strategy).
Double-check SDK code for variant handling
-
Verify that your application code correctly handles the feature flag variant response. Consult your specific SDK's documentation.
-
For example, using the Unleash React SDK, you might follow the check variants section. Given the example variants "A" and "B", your code might look like this:
import { useVariant } from '@unleash/proxy-client-react';
export const TestComponent = () => {
const variant = useVariant('ab-test-flag'); // 'ab-test-flag' is your feature flag name
if (variant.name === 'A') {
return <AComponent />;
} else if (variant.name === 'B') {
return <BComponent />;
}
// Fallback or default component if the flag is off or variant is not recognized
return <DefaultComponent />;
};
Use the Unleash playground
- If results are still unexpected, use the Playground to simulate different user contexts and verify that the feature flag and its variants are resolving as intended.
My requests are blocked due to CORS issues
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) issues can prevent your client-side application from communicating with the Unleash API or Edge. Browsers enforce CORS as a security measure. If you see errors like "No 'Access-Control-Policy' header is present on the requested resource," it's likely a CORS misconfiguration.
Configuring CORS in the Unleash admin UI (for Unleash server)
- Navigate to Settings in the Unleash Admin Dashboard.
- Select CORS Origins.
- Define the allowed origins (e.g.,
https://your-app.com).- For troubleshooting: You can temporarily set the allowed origin to
*(a single asterisk) to allow all origins. This helps confirm if CORS is the root cause. - Important Security Note: Using
*in production is generally discouraged. Always restrict origins to only those that require access.
- For troubleshooting: You can temporarily set the allowed origin to
- These settings can also be managed via the Unleash API.
Configuring CORS for Unleash Edge
If you are using Unleash Edge, CORS headers are typically configured via command-line flags when starting the Edge instance:
- To allow a specific origin:
unleash-edge edge --cors-origin "[https://your-application.com](https://your-application.com)" - You can specify multiple domains as a comma-separated list or by using the
--cors-originflag multiple times. - Other CORS-related headers (e.g.,
Access-Control-Allow-Headers,Access-Control-Allow-Methods) can also be set via command-line arguments. Refer to the Unleash Edge deployment documentation for details.
Verifying the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header
You can use the curl command-line tool to inspect the response headers from your Unleash instance and verify the CORS configuration. Replace <host> and <endpoint> with your Unleash server URL and a relevant API endpoint (e.g., the frontend API endpoint).